%matplotlib inline
from pssm.dglm import NormalDLM, PoissonDLM, BinomialDLM, CompositeDLM
from pssm.structure import UnivariateStructure, MultivariateStructure
import numpy as np
from scipy.stats import multivariate_normal as mvn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] =(12,4)
np.random.seed(42)
Dynamic Generalised Linear Models¶
Dynamic Linear Models¶
Dynamic linear models are a specific instance of state-space models where the observation and states are defined by
\begin{aligned} Y_t|\theta_t,\Phi_t &\sim \mathcal{N}\left(\theta_t; \mathsf{F}^T\theta_{t}, V\right) \ \theta_t|\theta_{t-1},\Phi_t &\sim \mathcal{N}\left(\theta_t;\mathsf{G}\theta_{t-1}, \mathsf{W}\right) \end{aligned}
Locally constant¶
The locally constant DLM corresponds to a simple state random walk, where the structure is defined by
\begin{aligned} \mathsf{F} &= \begin{bmatrix}1\end{bmatrix} \ \mathsf{G} &= \begin{bmatrix}1\end{bmatrix} \end{aligned}
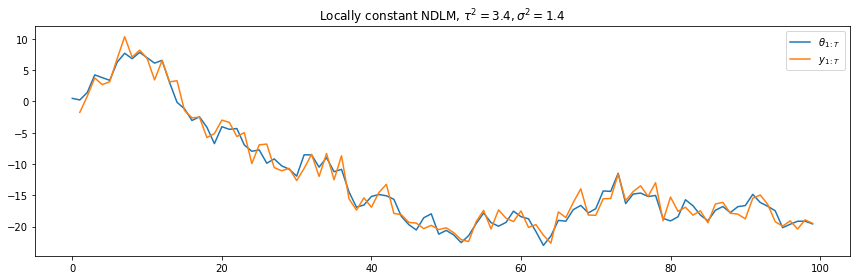
This can be specified by using (in this case with a state variance of \(\tau^2=3.4\)):
lc = {'structure': UnivariateStructure.locally_constant(3.4)}
print("F = {}, G = {}".format(lc['structure'].F, lc['structure'].G))
F = [[1]], G = [[1]]
We can then instantiate a DLM (with observation variance \(\sigma^2=1.4\)):
ndlm = NormalDLM(structure=lc['structure'], V=1.4)
Assuming we have a state prior of
we can then generate the states \(\theta_{1:T}\) and observation \(y_{1:T}\):
# the initial state prior
m0 = np.array([0])
C0 = np.matrix([[1]])
state0 = mvn(m0, C0).rvs()
lc['states'] = [state0]
for t in range(1, 100):
lc['states'].append(ndlm.state(lc['states'][t-1]))
lc['obs'] = [None]
for t in range(1, 100):
lc['obs'].append(ndlm.observation(lc['states'][t]))
t = range(100)
plt.plot(t, lc['states'])
plt.plot(t, lc['obs'])
plt.legend([r"$\theta_{1:T}$", r"$y_{1:T}$"], loc=1)
plt.title(r"Locally constant NDLM, $\tau^2=3.4, \sigma^2=1.4$")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
/Users/rcardoso/.pyenv/versions/documentation/lib/python3.7/site-packages/numpy/core/_asarray.py:136: VisibleDeprecationWarning: Creating an ndarray from ragged nested sequences (which is a list-or-tuple of lists-or-tuples-or ndarrays with different lengths or shapes) is deprecated. If you meant to do this, you must specify 'dtype=object' when creating the ndarray
return array(a, dtype, copy=False, order=order, subok=True)
Locally linear¶
A locally linear structure incorporates both an underlying mean and a trend. In this case the structure corresponds to
If we assume a state covariance of
we can create the structure as:
ll = {'structure': UnivariateStructure.locally_linear(W=np.matrix([[0.1, 0], [0, 0.1]]))}
and the Normal DLM structure can be created (with a state variance of \(\sigma^2=2.5\)) using:
ndlm = NormalDLM(structure=ll['structure'], V=2.5)
In this case we will assume a state prior of $\( \theta_0 \sim \mathcal{N}\left(\begin{bmatrix}0 & -1\end{bmatrix}, \begin{bmatrix}1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\right) \)$ and we can generate the states and observations as:
# the initial state prior
m0 = np.array([0, -1])
C0 = np.identity(2)
state0 = mvn(m0, C0).rvs()
ll['states'] = [state0]
for t in range(1, 100):
ll['states'].append(ndlm.state(ll['states'][t-1]))
ll['obs'] = [None]
for t in range(1, 100):
ll['obs'].append(ndlm.observation(ll['states'][t]))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
t=range(100)
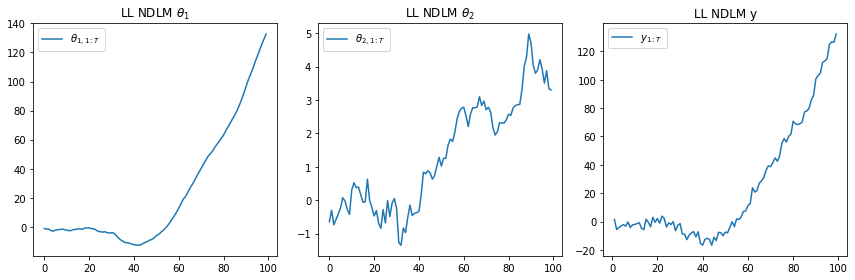
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.plot(t, [state[0] for state in ll['states']])
plt.legend([r"$\theta_{1,1:T}$"], loc=0)
plt.title(r"LL NDLM $\theta_1$")
plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)
plt.plot(t, [state[1] for state in ll['states']])
plt.legend([r"$\theta_{2,1:T}$"], loc=0)
plt.title(r"LL NDLM $\theta_2$")
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
plt.plot(range(100), ll['obs'])
plt.legend([r"$y_{1:T}$"], loc=0)
plt.title(r"LL NDLM y")
plt.tight_layout()
Fourier seasonality¶
fourier = {'structure': UnivariateStructure.cyclic_fourier(period=10, harmonics=2, W=np.identity(4))}
print("F(fourier) = {}".format(fourier['structure'].F))
print("G(fourier) = {}".format(fourier['structure'].G))
F(fourier) = [[1.]
[0.]
[1.]
[0.]]
G(fourier) = [[ 0.80901699 0.58778525 0. 0. ]
[-0.58778525 0.80901699 0. 0. ]
[ 0. 0. 0.30901699 0.95105652]
[ 0. 0. -0.95105652 0.30901699]]
ndlm_comp = NormalDLM(structure=(lc['structure']+fourier['structure']), V=2.5)
# the initial state prior
m0 = np.array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0])
C0 = np.identity(5)
state0 = np.random.multivariate_normal(m0, C0)
fourier['states'] = [state0]
for t in range(1, 100):
fourier['states'].append(ndlm_comp.state(fourier['states'][t-1]))
fourier['obs'] = [None]
for t in range(1, 100):
fourier['obs'].append(ndlm_comp.observation(fourier['states'][t]))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(range(100), fourier['states'])
plt.plot(range(100), fourier['obs'])
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x11f965c18>]
ARMA¶
ARMA(1)¶
Normal DLM¶
arma1 = {'structure': UnivariateStructure.arma(p=1, betas=[0.3], W=2.5)}
print("F(ARMA(1)) = {}".format(arma1['structure'].F))
print("G(ARMA(1)) = {}".format(arma1['structure'].G))
print("W(ARMA(1)) = {}".format(arma1['structure'].W))
F(ARMA(1)) = [[1.]]
G(ARMA(1)) = [[0.3]]
W(ARMA(1)) = [[2.5]]
# the initial state prior
m0 = np.array([0])
C0 = np.identity(1)
state0 = mvn(m0, C0).rvs()
ndlm_arma1 = NormalDLM(structure=(arma1['structure']), V=2.5)
arma1['states'] = [state0]
for t in range(1, 100):
arma1['states'].append(ndlm_arma1.state(arma1['states'][t-1]))
arma1['obs'] = [None]
for t in range(1, 100):
arma1['obs'].append(ndlm_arma1.observation(arma1['states'][t]))
t = range(100)
plt.plot(t, arma1['states'])
plt.plot(t, arma1['obs'])
plt.legend([r"$\theta_{1:T}$", r"$y_{1:T}$"], loc=1)
plt.title(r"ARMA(1) NDLM, $\tau^2=2.5, \sigma^2=2.5$")
plt.tight_layout()
Poisson DLM¶
# the initial state prior
m0 = np.array([0])
C0 = np.identity(1)
state0 = mvn(m0, C0).rvs()
podlm_arma1 = PoissonDLM(structure=(arma1['structure']))
arma1['states'] = [state0]
for t in range(1, 100):
arma1['states'].append(podlm_arma1.state(arma1['states'][t-1]))
arma1['obs'] = [None]
for t in range(1, 100):
arma1['obs'].append(podlm_arma1.observation(arma1['states'][t]))
t = range(100)
plt.plot(t, arma1['states'])
plt.plot(t, arma1['obs'], 'bo')
plt.legend([r"$\theta_{1:T}$", r"$y_{1:T}$"], loc=1)
plt.title(r"ARMA(1) PoDLM, $\tau^2=2.5")
plt.tight_layout()
ARMA(2)¶
Normal DLM¶
arma2 = {'structure': UnivariateStructure.arma(p=2, betas=[0.3, 0.2], W=2.5)}
print("F(ARMA(2)) = {}".format(arma2['structure'].F))
print("G(ARMA(2)) = {}".format(arma2['structure'].G))
print("W(ARMA(2)) = {}".format(arma2['structure'].W))
F(ARMA(2)) = [[1.]
[0.]]
G(ARMA(2)) = [[0.3 0.2]
[1. 0. ]]
W(ARMA(2)) = [[2.5 0. ]
[0. 0. ]]
# the initial state prior
m0 = np.array([0, 0])
C0 = np.identity(2)
state0 = mvn(m0, C0).rvs()
ndlm_arma2 = NormalDLM(structure=(arma2['structure']), V=2.5)
arma2['states'] = [state0]
for t in range(1, 100):
arma2['states'].append(ndlm_arma2.state(arma2['states'][t-1]))
arma2['obs'] = [None]
for t in range(1, 100):
arma2['obs'].append(ndlm_arma2.observation(arma2['states'][t]))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
t=range(100)
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.plot(t, [state[0] for state in arma2['states']])
plt.legend([r"$\theta_{1,1:T}$"], loc=0)
plt.title(r"ARMA(2) NDLM $\theta_1$")
plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)
plt.plot(t, [state[1] for state in arma2['states']])
plt.legend([r"$\theta_{2,1:T}$"], loc=0)
plt.title(r"ARMA(2) NDLM $\theta_2$")
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
plt.plot(range(100), arma2['obs'])
plt.legend([r"$y_{1:T}$"], loc=0)
plt.title(r"ARMA(2) NDLM y")
plt.tight_layout()
Poisson DLM¶
# the initial state prior
m0 = np.array([0, 0])
C0 = np.identity(2)
state0 = mvn(m0, C0).rvs()
podlm_arma2 = PoissonDLM(structure=(arma2['structure']))
arma2['states'] = [state0]
for t in range(1, 100):
arma2['states'].append(podlm_arma2.state(arma2['states'][t-1]))
arma2['obs'] = [None]
for t in range(1, 100):
arma2['obs'].append(podlm_arma2.observation(arma2['states'][t]))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
t=range(100)
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.plot(t, [state[0] for state in arma2['states']])
plt.legend([r"$\theta_{1,1:T}$"], loc=0)
plt.title(r"ARMA(2) PoDLM $\theta_1$")
plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)
plt.plot(t, [state[1] for state in arma2['states']])
plt.legend([r"$\theta_{2,1:T}$"], loc=0)
plt.title(r"ARMA(2) PoDLM $\theta_2$")
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
plt.plot(range(100), arma2['obs'], 'bo')
plt.legend([r"$y_{1:T}$"], loc=0)
plt.title(r"ARMA(2) PoDLM y")
plt.tight_layout()
Filtering¶
Locally constant¶
from pssm.filters import KalmanFilter
kf = KalmanFilter(structure=lc['structure'], V=1.4)
m0 = np.array([0])
C0 = np.matrix([[1e3]])
filtered = {'ms': [m0], 'Cs': [C0]}
for t in range(1, 100):
m, C = kf.filter(y=lc['obs'][t], m=filtered['ms'][t-1], C=filtered['Cs'][t-1])
filtered['ms'].append(m)
filtered['Cs'].append(C)
t = range(100)
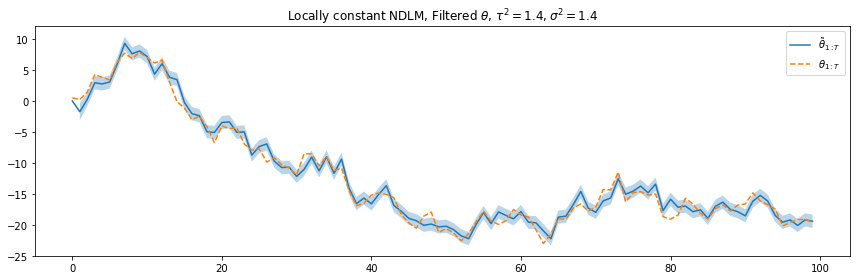
plt.plot(t, filtered['ms'])
plt.plot(t, lc['states'], '--')
lb = []
ub = []
for m, C in zip(filtered['ms'], filtered['Cs']):
lb.append((m[0] - C[0][0]).item())
ub.append((m[0] + C[0][0]).item())
plt.fill_between(t[1:], lb[1:], ub[1:], alpha=0.3)
plt.legend([r"$\tilde{\theta}_{1:T}$", r"$\theta_{1:T}$"], loc=1)
plt.title(r"Locally constant NDLM, Filtered $\theta$, $\tau^2=1.4, \sigma^2=1.4$")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Locally linear¶
kf = KalmanFilter(structure=ll['structure'], V=2.5)
m0 = np.array([0, 0])
C0 = np.diag([1e3, 1e3])
filtered = {'ms': [m0], 'Cs': [C0]}
for t in range(1, 100):
m, C = kf.filter(y=ll['obs'][t], m=filtered['ms'][t-1], C=filtered['Cs'][t-1])
filtered['ms'].append(m)
filtered['Cs'].append(C)
t=range(100)
lb = []
ub = []
for m, C in zip(filtered['ms'], filtered['Cs']):
lb.append((m[0] - C.item((0,0)), m[1] - C.item((1,1)),))
ub.append((m[0] + C.item((0,0)), m[1] + C.item((1,1)),))
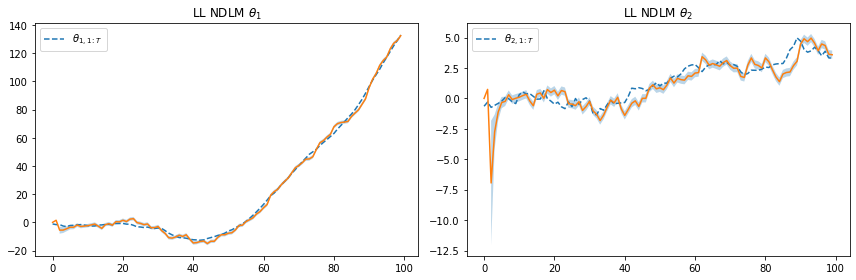
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(t, [state[0] for state in ll['states']], '--')
plt.plot(t, [state[0] for state in filtered['ms']])
plt.fill_between(t[2:], [b[0] for b in lb[2:]], [b[0] for b in ub[2:]], alpha=0.3)
plt.legend([r"$\theta_{1,1:T}$"], loc=0)
plt.title(r"LL NDLM $\theta_1$")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(t, [state[1] for state in ll['states']], '--')
plt.plot(t, [state[1] for state in filtered['ms']])
plt.fill_between(t[2:], [b[1] for b in lb[2:]], [b[1] for b in ub[2:]], alpha=0.3)
plt.legend([r"$\theta_{2,1:T}$"], loc=0)
plt.title(r"LL NDLM $\theta_2$")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Parameter estimation (FFBS)¶
Locally constant¶
FFBS estimation for a locally constant model.
from pssm.mc import *
m0 = np.array([0])
C0 = np.identity(1)*1000
ffbs = FFBS(lc['structure'], m0, C0, 0.001, [0.001], lc['obs'])
Vs = [1]
Ws = [np.identity(1)]
states = []
for i in range(1, 20):
W, V, _states = ffbs.run(V=Vs[i-1], W=Ws[i-1], states=True)
Ws.append(W)
Vs.append(V)
states.append(_states)
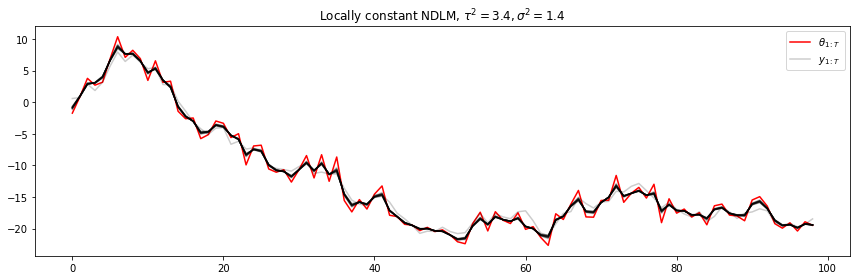
t = range(99)
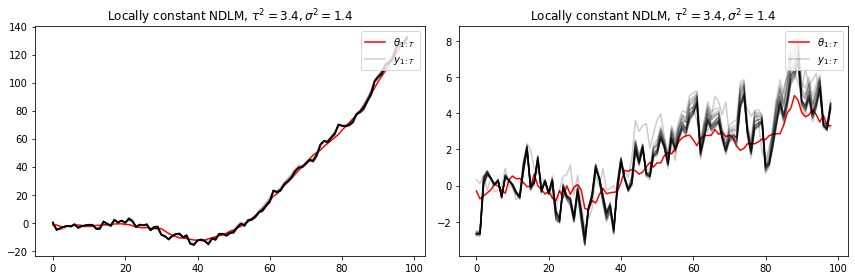
plt.plot(t, lc['obs'][1:], c='red')
for i in range(19):
plt.plot(t, states[i], c='black', alpha=0.2)
plt.legend([r"$\theta_{1:T}$", r"$y_{1:T}$"], loc=1)
plt.title(r"Locally constant NDLM, $\tau^2=3.4, \sigma^2=1.4$")
plt.tight_layout()
for i in range(20, 1000):
W, V = ffbs.run(V=Vs[i-1], W=Ws[i-1], states=False)
Ws.append(W)
Vs.append(V)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.hist(Vs, bins=50)
plt.axvline(x=np.mean(Vs), c='black', ls='--', alpha=0.75)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
_Ws = [W[0][0] for W in Ws]
plt.hist(_Ws, bins=50)
plt.axvline(x=np.mean(_Ws), c='black', ls='--', alpha=0.75)
plt.tight_layout()
Locally linear¶
from pssm.mc import *
m0 = np.array([0, 0])
C0 = np.identity(2)*1000
ffbs = FFBS(ll['structure'], m0, C0, 1.0, [1.0, 1.0], ll['obs'])
Vs = [1]
Ws = [np.identity(2)]
states = []
for i in range(1, 20):
W, V, _states = ffbs.run(V=Vs[i-1], W=Ws[i-1], states=True)
Ws.append(W)
Vs.append(V)
states.append(_states)
t = range(99)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(t, [s[0] for s in ll['states'][1:]], c='red')
for i in range(19):
plt.plot(t, [s[0] for s in states[i]], c='black', alpha=0.2)
plt.legend([r"$\theta_{1:T}$", r"$y_{1:T}$"], loc=1)
plt.title(r"Locally constant NDLM, $\tau^2=3.4, \sigma^2=1.4$")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(t, [s[1] for s in ll['states'][1:]], c='red')
for i in range(19):
plt.plot(t, [s[1] for s in states[i]], c='black', alpha=0.2)
plt.legend([r"$\theta_{1:T}$", r"$y_{1:T}$"], loc=1)
plt.title(r"Locally constant NDLM, $\tau^2=3.4, \sigma^2=1.4$")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
for i in range(20, 1000):
W, V = ffbs.run(V=Vs[i-1], W=Ws[i-1], states=False)
Ws.append(W)
Vs.append(V)
print("V (mean) = {}".format(np.mean(Vs)))
print("W1 (mean) = {}".format(np.mean([W[0][0] for W in Ws])))
print("W2 (mean) = {}".format(np.mean([W[1][1] for W in Ws])))
V (mean) = 0.0010238714463317758
W1 (mean) = 0.0010764040008501392
W2 (mean) = 0.0013080823464825782
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.hist(Vs, bins=50)
plt.axvline(x=np.mean(Vs), c='black', ls='--', alpha=0.75)
plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)
_Ws = [W[0][0] for W in Ws]
plt.hist(_Ws, bins=50)
plt.axvline(x=np.mean(_Ws), c='black', ls='--', alpha=0.75)
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
_Ws = [W[1][1] for W in Ws]
plt.hist(_Ws, bins=50)
plt.axvline(x=np.mean(_Ws), c='black', ls='--', alpha=0.75)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()

Non-linear models¶
Poisson DLM¶
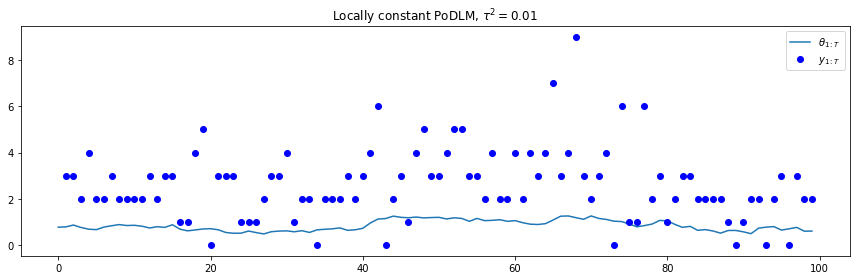
plc = {'structure': UnivariateStructure.locally_constant(0.01)}
podlm = PoissonDLM(structure=plc['structure'])
# the initial state prior
m0 = np.array([0])
C0 = np.matrix([[1]])
state0 = mvn(m0, C0).rvs()
plc['states'] = [state0]
for t in range(1, 100):
plc['states'].append(podlm.state(plc['states'][t-1]))
plc['obs'] = [None]
for t in range(1, 100):
plc['obs'].append(podlm.observation(plc['states'][t]))
t = range(100)
plt.plot(t, plc['states'])
plt.plot(t, plc['obs'], 'bo')
plt.legend([r"$\theta_{1:T}$", r"$y_{1:T}$"], loc=1)
plt.title(r"Locally constant PoDLM, $\tau^2=0.01$")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Binomial DLM¶
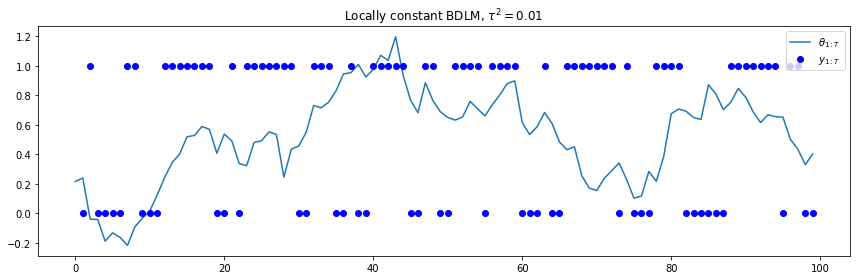
bdlm = BinomialDLM(structure=plc['structure'], categories=1)
# the initial state prior
m0 = np.array([0])
C0 = np.matrix([[1]])
state0 = mvn(m0, C0).rvs()
plc['states'] = [state0]
for t in range(1, 100):
plc['states'].append(bdlm.state(plc['states'][t-1]))
plc['obs'] = [None]
for t in range(1, 100):
plc['obs'].append(bdlm.observation(plc['states'][t]))
t = range(100)
plt.plot(t, plc['states'])
plt.plot(t, plc['obs'], 'bo')
plt.legend([r"$\theta_{1:T}$", r"$y_{1:T}$"], loc=1)
plt.title(r"Locally constant BDLM, $\tau^2=0.01$")
plt.tight_layout()
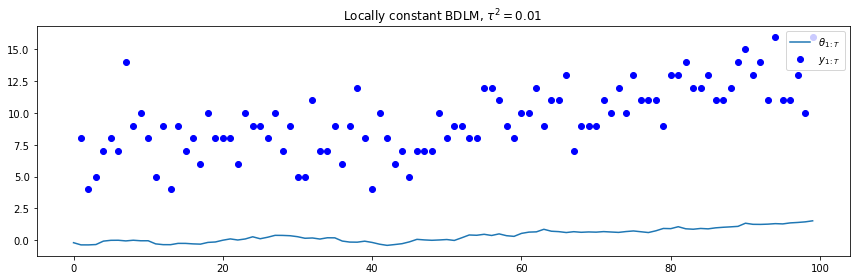
bdlm = BinomialDLM(structure=plc['structure'], categories=16)
# the initial state prior
m0 = np.array([0])
C0 = np.matrix([[5]])
state0 = mvn(m0, C0).rvs()
plc['states'] = [state0]
for t in range(1, 100):
plc['states'].append(bdlm.state(plc['states'][t-1]))
plc['obs'] = [None]
for t in range(1, 100):
plc['obs'].append(bdlm.observation(plc['states'][t]))
t = range(100)
plt.plot(t, plc['states'])
plt.plot(t, plc['obs'], 'bo')
plt.legend([r"$\theta_{1:T}$", r"$y_{1:T}$"], loc=1)
plt.title(r"Locally constant BDLM, $\tau^2=0.01$")
plt.tight_layout()
Composite (multivariate) DGLMs¶
comp_lc = UnivariateStructure.locally_constant(W=0.3)
comp_seasonal = UnivariateStructure.cyclic_fourier(period=50, harmonics=2, W=np.eye(4))
comp_ndlm = NormalDLM(structure=comp_lc + comp_seasonal, V=2.3)
comp_bdlm = BinomialDLM(structure=comp_lc, categories=4)
composite = CompositeDLM(comp_ndlm, comp_bdlm)
# the initial state prior
m0 = np.array([0.0]*6)
C0 = np.eye(6)
state0 = mvn(m0, C0).rvs()
comp_states = [state0]
for t in range(1, 100):
comp_states.append(composite.state(comp_states[t-1]))
comp_obs = [None]
for t in range(1, 100):
comp_obs.append(composite.observation(comp_states[t]))
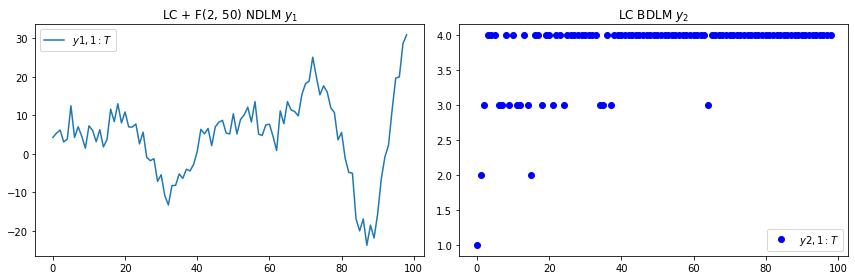
t=range(99)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(t, [y[0] for y in comp_obs[1:]])
plt.legend([r"$y{1,1:T}$"], loc=0)
plt.title(r"LC + F(2, 50) NDLM $y_1$")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(t, [y[1] for y in comp_obs[1:]], 'bo')
plt.legend([r"$y{2,1:T}$"], loc=0)
plt.title(r"LC BDLM $y_2$")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()